第 5 章:工具使用(函数调用)
工具使用模式概述
截至目前,我们探讨的 Agent 模式主要聚焦于语言模型间的交互编排及 Agent 内部工作流的信息管理(链式、路由、并行化、反思)。然而,要让 Agent 真正发挥价值并与现实世界或外部系统互动,它们需要具备工具使用能力。
工具使用模式通常通过函数调用机制实现,使 Agent 能连接外部 API、数据库、服务,甚至执行代码。该机制让位于 Agent 核心的大语言模型(LLM)能基于用户请求或任务状态,决策何时以及如何调用特定外部函数。
该过程通常包括:
工具定义: 外部函数或能力被定义并描述给 LLM。此描述包括函数的目的、名称以及它接受的参数及其类型和描述。LLM 决策: LLM 接收用户的请求和可用的工具定义。基于其对请求和工具的理解,LLM 决定是否需要调用一个或多个工具来满足请求。函数调用生成: 如果 LLM 决定使用工具,它会生成一个结构化输出(通常是 JSON 对象),指定要调用的工具名称和要传递给它的参数(参数),这些参数从用户的请求中提取。工具执行: Agent 框架或编排层拦截此结构化输出。它识别请求的工具并使用提供的参数执行实际的外部函数。观察/结果: 工具执行的输出或结果返回给 Agent。LLM 处理(可选但常见): LLM 接收工具的输出作为上下文,并使用它向用户制定最终响应或决定工作流中的下一步(可能涉及调用另一个工具、反思或提供最终答案)。
此模式是基础性的,因为它打破了 LLM 训练数据的限制,允许它访问最新信息、执行它内部无法完成的计算、与用户特定数据交互或触发现实世界的行动。函数调用是连接 LLM 推理能力与可用的大量外部功能之间差距的技术机制。
虽然"函数调用"精确描述了调用预定义代码函数的过程,但采用更广泛的"工具调用"概念更具实践价值。这一概念承认 Agent 的能力远超简单函数执行范畴——"工具"既可以是传统函数,也可以是复杂的 API 端点、数据库查询请求,甚至是向其他专业 Agent 发送的指令。这种视角帮助我们构建更复杂的系统,例如主 Agent 可将数据分析任务委托给专用"分析师 Agent",或通过 API 查询外部知识库。以"工具调用"的思维方式,能更全面把握 Agent 作为跨数字资源和智能实体生态系统的编排者潜力。
像 LangChain、LangGraph 和 Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) 这样的框架为定义工具并将它们集成到 Agent 工作流中提供了强大的支持,通常利用现代 LLM(如 Gemini 或 OpenAI 系列中的那些)的原生函数调用能力。在这些框架的"画布"上,您定义工具,然后配置 Agent(通常是 LLM Agent)以意识到并能够使用这些工具。
工具使用是构建强大、交互式且具环境感知能力 Agent 的基础模式。
实际应用与用例
工具使用模式几乎适用于 Agent 需要超越生成文本来执行操作或检索特定动态信息的任何场景:
从外部源检索信息:
用例: 天气 Agent。
工具: 接受位置并返回当前天气状况的天气 API。Agent 流程: 用户问"伦敦的天气如何?",LLM 识别需要天气工具,用"伦敦"调用工具,工具返回数据,LLM 将数据格式化为用户友好的响应。
与数据库和 API 交互:
用例: 电子商务 Agent。
工具: API 调用以检查产品库存、获取订单状态或处理付款。Agent 流程: 用户问"产品 X 有库存吗?",LLM 调用库存 API,工具返回库存数量,LLM 告诉用户库存状态。
执行计算和数据分析:
用例: 金融 Agent。
工具: 计算器函数、股票市场数据 API、电子表格工具。Agent 流程: 用户问"AAPL 的当前价格是多少,如果我以 150 美元购买 100 股,计算潜在利润?",LLM 调用股票 API,获取当前价格,然后调用计算器工具,获取结果,格式化响应。
发送通信:
用例: 个人助理 Agent。
工具: 电子邮件发送 API。Agent 流程: 用户说"给 John 发一封关于明天会议的电子邮件。",LLM 使用从请求中提取的收件人、主题和正文调用电子邮件工具。
执行代码:
用例: 编码助手 Agent。
工具: 代码解释器。Agent 流程: 用户提供 Python 代码片段并问"这段代码做什么?",LLM 使用解释器工具运行代码并分析其输出。
控制其他系统或设备:
用例: 智能家居 Agent。
工具: 控制智能灯的 API。Agent 流程: 用户说"关闭客厅的灯。"LLM 使用命令和目标设备调用智能家居工具。
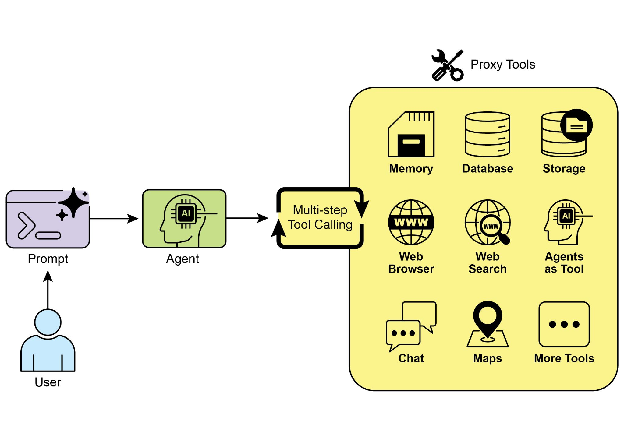
工具使用将语言模型从文本生成器转变为能够在数字或物理世界中感知、推理和行动的 Agent(见图 1)
图 1:Agent 使用工具的一些示例
实操代码示例(LangChain)
在 LangChain 框架中实现工具使用需分两步:首先定义工具(通常通过封装 Python 函数或其他可执行组件),随后将工具与语言模型绑定。这使得模型能在需要调用外部函数时,生成结构化的工具使用请求。
以下实现将通过定义一个简单的函数来模拟信息检索工具,以此演示此原理。随后,将构建并配置一个 Agent 以利用此工具响应用户输入。执行此示例需要安装核心 LangChain 库和特定于模型的提供程序包。此外,使用所选语言模型服务的适当身份验证(通常通过在本地环境中配置的 API 密钥)是必要的先决条件。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 import os, getpassimport asyncioimport nest_asynciofrom typing import List from dotenv import load_dotenvimport loggingfrom langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAIfrom langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatefrom langchain_core.tools import tool as langchain_toolfrom langchain.agents import create_tool_calling_agent, AgentExecutor"GOOGLE_API_KEY" ] = getpass.getpass("Enter your Google API key: " )"OPENAI_API_KEY" ] = getpass.getpass("Enter your OpenAI API key: " )try :"gemini-2.0-flash" , temperature=0 )print (f"✅ 语言模型已初始化:{llm.model} " )except Exception as e:print (f"🛑 初始化语言模型时出错:{e} " )None @langchain_tool def search_information (query: str ) -> str :""" 提供有关给定主题的事实信息。使用此工具查找诸如"法国首都"或"伦敦的天气?"等短语的答案。 """ print (f"\n--- 🛠️ 工具调用:search_information,查询:'{query} ' ---" )"weather in london" : "伦敦目前多云,温度为 15°C。" ,"capital of france" : "法国的首都是巴黎。" ,"population of earth" : "地球的估计人口约为 80 亿人。" ,"tallest mountain" : "珠穆朗玛峰是海拔最高的山峰。" ,"default" : f"'{query} ' 的模拟搜索结果:未找到特定信息,但该主题似乎很有趣。" "default" ])print (f"--- 工具结果:{result} ---" )return resultif llm:"system" , "你是一个有用的助手。" ),"human" , "{input}" ),"placeholder" , "{agent_scratchpad}" ),True , tools=tools)async def run_agent_with_tool (query: str ):"""使用查询调用 Agent 执行器并打印最终响应。""" print (f"\n--- 🏃 使用查询运行 Agent:'{query} ' ---" )try :await agent_executor.ainvoke({"input" : query})print ("\n--- ✅ 最终 Agent 响应 ---" )print (response["output" ])except Exception as e:print (f"\n🛑 Agent 执行期间发生错误:{e} " )async def main ():"""并发运行所有 Agent 查询。""" "法国的首都是什么?" ),"伦敦的天气怎么样?" ),"告诉我一些关于狗的事情。" ) await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
代码使用 LangChain 库和 Google Gemini 模型设置了一个工具调用 Agent。它定义了一个 search_information 工具,模拟为特定查询提供事实答案。该工具对"weather in london"、"capital of france"和"population of earth"有预定义的响应,以及其他查询的默认响应。初始化了一个 ChatGoogleGenerativeAI 模型,确保其具有工具调用能力。创建了一个 ChatPromptTemplate 来指导 Agent 的交互。使用 create_tool_calling_agent 函数将语言模型、工具和提示词组合成一个 Agent。然后设置一个 AgentExecutor 来管理 Agent 的执行和工具调用。定义了 run_agent_with_tool 异步函数以使用给定查询调用 Agent 并打印结果。main 异步函数准备多个要并发运行的查询。这些查询旨在测试 search_information 工具的特定和默认响应。最后,asyncio.run(main()) 调用执行所有 Agent 任务。代码包括在继续 Agent 设置和执行之前成功 LLM 初始化的检查。
实操代码示例(CrewAI)
此代码演示了在 CrewAI 框架中实现函数调用(工具)的具体案例。通过设置简单场景:让配备信息查询工具的 Agent 获取模拟股价,展示核心实现逻辑。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 import osfrom crewai import Agent, Task, Crewfrom crewai.tools import toolimport loggingformat ='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s' )@tool("Stock Price Lookup Tool" def get_stock_price (ticker: str ) -> float :""" 获取给定股票代码符号的最新模拟股票价格。 以浮点数形式返回价格。如果未找到代码,则引发 ValueError。 """ f"工具调用:get_stock_price,代码为 '{ticker} '" )"AAPL" : 178.15 ,"GOOGL" : 1750.30 ,"MSFT" : 425.50 ,if price is not None :return priceelse :raise ValueError(f"未找到代码 '{ticker.upper()} ' 的模拟价格。" )'高级财务分析师' ,'使用提供的工具分析股票数据并报告关键价格。' ,"你是一位经验丰富的财务分析师,擅长使用数据源查找股票信息。你提供清晰、直接的答案。" ,True ,False ,"Apple(代码:AAPL)的当前模拟股票价格是多少?" "使用 'Stock Price Lookup Tool' 查找它。" "如果未找到代码,你必须报告无法检索价格。" "一个清晰的句子,说明 AAPL 的模拟股票价格。" "例如:'AAPL 的模拟股票价格是 $178.15。'" "如果无法找到价格,请明确说明。" True def main ():"""运行团队的主函数。""" if not os.environ.get("OPENAI_API_KEY" ):print ("错误:未设置 OPENAI_API_KEY 环境变量。" )print ("请在运行脚本之前设置它。" )return print ("\n## 启动财务团队..." )print ("---------------------------------" )print ("\n---------------------------------" )print ("## 团队执行完成。" )print ("\n最终结果:\n" , result)if __name__ == "__main__" :
此代码演示了使用 CrewAI 库模拟财务分析任务的简单应用程序。它定义了一个自定义工具 get_stock_price,模拟查找预定义股票代码的价格。该工具设计为对有效代码返回浮点数,或对无效代码引发 ValueError。创建了一个名为 financial_analyst_agent 的 CrewAI Agent,角色为高级财务分析师。该 Agent 被赋予 get_stock_price 工具进行交互。定义了一个任务 analyze_aapl_task,专门指示 Agent 使用工具查找 AAPL 的模拟股票价格。任务描述包括关于使用工具时如何处理成功和失败情况的明确说明。组建了一个团队,包含 financial_analyst_agent 和 analyze_aapl_task。为 Agent 和团队启用了详细设置,以在执行期间提供详细日志。脚本的主要部分在标准 if name == "main ": 块中使用 kickoff() 方法运行团队的任务。在启动团队之前,它会检查是否设置了 OPENAI_API_KEY 环境变量,这是 Agent 运行所必需的。然后将团队执行的结果(即任务的输出)打印到控制台。代码还包括基本日志配置,以更好地跟踪团队的行动和工具调用。它使用环境变量进行 API 密钥管理,尽管它指出对于生产环境建议使用更安全的方法。简而言之,核心逻辑展示了如何定义工具、Agent 和任务,以在 CrewAI 中创建协作工作流。
实操代码(Google ADK)
Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) 提供原生集成工具库,可直接扩展 Agent 能力。
Google 搜索: 此类组件的主要示例是 Google 搜索工具。此工具作为 Google 搜索引擎的直接接口,为 Agent 提供执行网络搜索和检索外部信息的功能。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 from google.adk.agents import Agentfrom google.adk.runners import Runnerfrom google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionServicefrom google.adk.tools import google_searchfrom google.genai import typesimport nest_asyncioimport asyncio"Google Search_agent" "user1234" "1234" "basic_search_agent" ,"gemini-2.0-flash-exp" ,"使用 Google 搜索回答问题的 Agent。" ,"我可以通过搜索互联网回答您的问题。随便问我什么!" ,async def call_agent (query ):""" 使用查询调用 Agent 的辅助函数。 """ await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)'user' , parts=[types.Part(text=query)])for event in events:if event.is_final_response():0 ].textprint ("Agent 响应:" , final_response)"最新的 AI 新闻是什么?" ))
此代码演示了如何使用 Python 的 Google ADK 创建和使用由 Google ADK 驱动的基本 Agent。该 Agent 设计为通过利用 Google 搜索作为工具来回答问题。首先,从 IPython、google.adk 和 google.genai 导入必要的库。定义了应用程序名称、用户 ID 和会话 ID 的常量。创建了一个名为"basic_search_agent"的 Agent 实例,带有描述和说明指示其目的。它被配置为使用 Google 搜索工具,这是 ADK 提供的预构建工具。初始化 InMemorySessionService(见第 8 章)以管理 Agent 的会话。为指定的应用程序、用户和会话 ID 创建新会话。实例化 Runner,将创建的 Agent 与会话服务链接。此运行器负责在会话中执行 Agent 的交互。定义了辅助函数 call_agent 以简化向 Agent 发送查询和处理响应的过程。在 call_agent 内部,用户的查询被格式化为具有角色"user"的 types.Content 对象。使用用户 ID、会话 ID 和新消息内容调用 runner.run 方法。runner.run 方法返回表示 Agent 操作和响应的事件列表。代码遍历这些事件以查找最终响应。如果事件被识别为最终响应,则提取该响应的文本内容。提取的 Agent 响应然后打印到控制台。最后,使用查询"最新的 AI 新闻是什么?"调用 call_agent 函数以演示 Agent 的运行情况。
代码执行: Google ADK 包含专为动态代码执行设计的组件。built_in_code_execution 工具提供沙盒化 Python 解释器,让模型能编写运行代码执行计算、操作数据结构及运行脚本。此功能对需要确定性逻辑和精确计算的任务至关重要,弥补了概率性语言生成的不足。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 import os, getpassimport asyncioimport nest_asynciofrom typing import List from dotenv import load_dotenvimport loggingfrom google.adk.agents import LlmAgent from google.adk.runners import Runnerfrom google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionServicefrom google.adk.tools import google_searchfrom google.adk.code_executors import BuiltInCodeExecutorfrom google.genai import types"calculator" "user1234" "session_code_exec_async" "calculator_agent" ,"gemini-2.0-flash" ,"""你是一个计算器 Agent。 当给定数学表达式时,编写并执行 Python 代码来计算结果。 仅返回最终的数值结果作为纯文本,不带 markdown 或代码块。 """ ,"执行 Python 代码以进行计算。" ,async def call_agent_async (query ):await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)'user' , parts=[types.Part(text=query)])print (f"\n--- 运行查询:{query} ---" )"未捕获最终文本响应。" try :async for event in runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content):print (f"事件 ID:{event.id } ,作者:{event.author} " )if event.content and event.content.parts and event.is_final_response():for part in event.content.parts: if part.executable_code:print (f" 调试:Agent 生成的代码:\n```python\n{part.executable_code.code} \n```" )elif part.code_execution_result:print (f" 调试:代码执行结果:{part.code_execution_result.outcome} - 输出:\n{part.code_execution_result.output} " )elif part.text and not part.text.isspace():print (f" 文本:'{part.text.strip()} '" )for part in event.content.parts if part.text]"" .join(text_parts)print (f"==> 最终 Agent 响应:{final_result} " )except Exception as e:print (f"Agent 运行期间出错:{e} " )print ("-" * 30 )async def main ():await call_agent_async("计算 (5 + 7) * 3 的值" )await call_agent_async("10 的阶乘是多少?" )try :except RuntimeError as e:if "cannot be called from a running event loop" in str (e):print ("\n在现有事件循环中运行(如 Colab/Jupyter)。" )print ("请在笔记本单元格中运行 `await main()` 代替。" )else :raise e
此脚本使用 Google 的 Agent Development Kit (ADK) 创建一个通过编写和执行 Python 代码解决数学问题的 Agent。它定义了一个 LlmAgent,专门指示其充当计算器,为其配备 built_in_code_execution 工具。主要逻辑位于 call_agent_async 函数中,该函数向 Agent 的运行器发送用户查询并处理结果事件。在此函数内部,异步循环遍历事件,打印生成的 Python 代码及其执行结果以进行调试。代码仔细区分这些中间步骤和包含数值答案的最终事件。最后,main 函数使用两个不同的数学表达式运行 Agent,以演示其执行计算的能力。
企业搜索: 此代码使用 Python 中的 google.adk 库定义了一个 Google ADK 应用程序。它专门使用 VSearchAgent,该 Agent 旨在通过搜索指定的 Vertex AI 搜索数据存储来回答问题。代码初始化一个名为"q2_strategy_vsearch_agent"的 VSearchAgent,提供描述、要使用的模型("gemini-2.0-flash-exp")和 Vertex AI 搜索数据存储的 ID。DATASTORE_ID 预期设置为环境变量。然后为 Agent 设置 Runner,使用 InMemorySessionService 管理对话历史。定义了异步函数 call_vsearch_agent_async 以与 Agent 交互。此函数接受查询,构造消息内容对象,并调用运行器的 run_async 方法将查询发送到 Agent。然后该函数将 Agent 的响应流式传输回控制台。它还打印有关最终响应的信息,包括来自数据存储的任何源归因。包含错误处理以捕获 Agent 执行期间的异常,提供有关潜在问题(如数据存储 ID 不正确或缺少权限)的信息性消息。提供了另一个异步函数 run_vsearch_example 以演示如何使用示例查询调用 Agent。主执行块检查 DATASTORE_ID 是否已设置,然后使用 asyncio.run 运行示例。它包括检查以处理在已有运行事件循环的环境(如 Jupyter 笔记本)中运行代码的情况。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 import asynciofrom google.genai import typesfrom google.adk import agentsfrom google.adk.runners import Runnerfrom google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionServiceimport os"DATASTORE_ID" )"vsearch_app" "user_123" "session_456" "q2_strategy_vsearch_agent" ,"使用 Vertex AI 搜索回答有关 Q2 战略文档的问题。" ,"gemini-2.0-flash-exp" , "temperature" : 0.0 }async def call_vsearch_agent_async (query: str ):"""初始化会话并流式传输 Agent 的响应。""" print (f"用户:{query} " )print ("Agent:" , end="" , flush=True )try :'user' , parts=[types.Part(text=query)])async for event in runner.run_async(if hasattr (event, 'content_part_delta' ) and event.content_part_delta:print (event.content_part_delta.text, end="" , flush=True )if event.is_final_response():print () if event.grounding_metadata:print (f" (来源归因:找到 {len (event.grounding_metadata.grounding_attributions)} 个来源)" )else :print (" (未找到基础元数据)" )print ("-" * 30 )except Exception as e:print (f"\n发生错误:{e} " )print ("请确保您的数据存储 ID 正确,并且服务帐户具有必要的权限。" )print ("-" * 30 )async def run_vsearch_example ():await call_vsearch_agent_async("总结 Q2 战略文档的要点。" )await call_vsearch_agent_async("实验室 X 提到了哪些安全程序?" )if __name__ == "__main__" :if not DATASTORE_ID:print ("错误:未设置 DATASTORE_ID 环境变量。" )else :try :except RuntimeError as e:if "cannot be called from a running event loop" in str (e):print ("在运行事件循环中跳过执行。请直接运行此脚本。" )else :raise e
总的来说,此代码为构建利用 Vertex AI 搜索根据存储在数据存储中的信息回答问题的对话式 AI 应用程序提供了基本框架。它演示了如何定义 Agent、设置运行器以及在流式传输响应的同时异步与 Agent 交互。重点是从特定数据存储检索和综合信息以回答用户查询。
Vertex Extensions: Vertex AI 扩展是一个结构化的 API 包装器,使模型能够连接到外部 API 以进行实时数据处理和操作执行。扩展提供企业级安全性、数据隐私和性能保证。它们可用于生成和运行代码、查询网站以及分析来自私有数据存储的信息等任务。Google 为常见用例提供预构建扩展,如代码解释器和 Vertex AI 搜索,并可选择创建自定义扩展。扩展的主要好处包括强大的企业控制和与其他 Google 产品的无缝集成。扩展和函数调用之间的关键区别在于它们的执行:Vertex AI 自动执行扩展,而函数调用需要用户或客户端手动执行。
概览
是什么: 大型语言模型(LLM)是强大的文本生成器,但它们基本上与外部世界断开连接。它们的知识是静态的,仅限于训练数据,并且缺乏执行操作或检索实时信息的能力。这种固有的限制阻止它们完成需要与外部 API、数据库或服务交互的任务。没有通往这些外部系统的桥梁,它们解决现实世界问题的效用受到严重限制。
为什么: 工具使用模式(通常通过函数调用实现)为此问题提供了标准化解决方案。它的工作原理是以 LLM 可以理解的方式向其描述可用的外部函数或"工具"。基于用户的请求,Agent LLM 可以决定是否需要工具,并生成指定要调用哪个函数以及使用什么参数的结构化数据对象(如 JSON)。编排层执行此函数调用,检索结果,并将其反馈给 LLM。这允许 LLM 将最新的外部信息或操作结果合并到其最终响应中,有效地赋予其行动能力。
经验法则: 当 Agent 需要突破 LLM 的内部知识并与外部世界交互时,使用工具使用模式。这对于需要实时数据(例如,检查天气、股票价格)、访问私有或专有信息(例如,查询公司数据库)、执行精确计算、执行代码或触发其他系统中的操作(例如,发送电子邮件、控制智能设备)的任务至关重要。
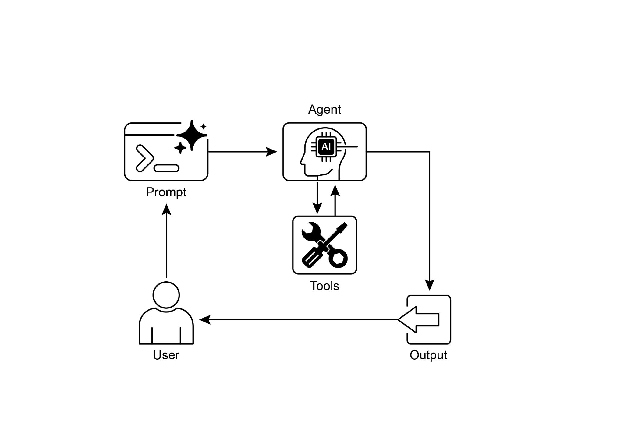
视觉摘要:
图 2:工具使用设计模式
关键要点
工具使用(函数调用)允许 Agent 与外部系统交互并访问动态信息。
它涉及定义具有 LLM 可以理解的清晰描述和参数的工具。
LLM 决定何时使用工具并生成结构化函数调用。
Agent 框架执行实际的工具调用并将结果返回给 LLM。
工具使用对于构建可以执行现实世界操作并提供最新信息的 Agent 至关重要。
LangChain 使用 @tool 装饰器简化工具定义,并提供 create_tool_calling_agent 和 AgentExecutor 用于构建工具使用 Agent。
Google ADK 有许多非常有用的预构建工具,如 Google 搜索、代码执行和 Vertex AI 搜索工具。
结论
工具使用模式是将大型语言模型的功能范围扩展到其固有文本生成能力之外的关键架构原则。通过为模型配备与外部软件和数据源交互的能力,此范式允许 Agent 执行操作、进行计算并从其他系统检索信息。此过程涉及模型在确定满足用户查询需要时生成调用外部工具的结构化请求。LangChain、Google ADK 和 CrewAI 等框架提供结构化抽象和组件,促进这些外部工具的集成。这些框架管理向模型公开工具规范并解析其后续工具使用请求的过程。这简化了可以与外部数字环境交互并在其中采取行动的复杂 Agent 系统的开发。
参考文献
LangChain Documentation (Tools): https://python.langchain.com/docs/integrations/tools/
Google Agent Developer Kit (ADK) Documentation (Tools): https://google.github.io/adk-docs/tools/
OpenAI Function Calling Documentation: https://platform.openai.com/docs/guides/function-calling
CrewAI Documentation (Tools): https://docs.crewai.com/concepts/tools
返回目录页